DNA REPLICATION
DNA Replication is the biological process by which DNA makes
a copy of itself during cell division. DNA is made up of a double helix of two
complementary strands. Process replication starts by separating the double
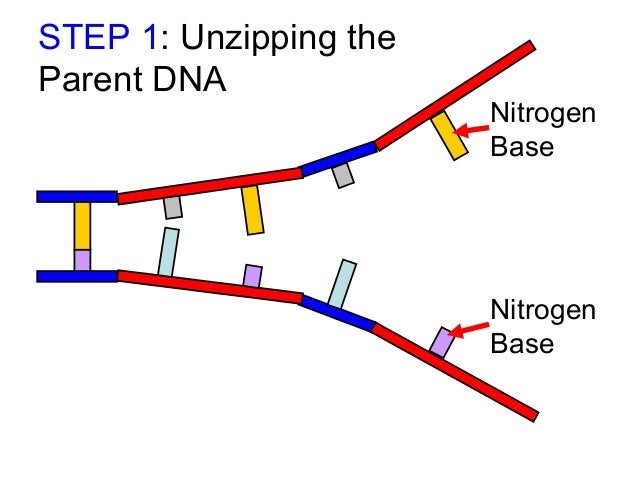
helix structure of the DNA molecules. This step is known as DNA unzipping. DNA
unzipping is the casual term used where the denaturation of double stranded DNA
takes place. This is carried out by an enzyme called helicase which breaks the
hydrogen bonds holding the complementary bases of DNA together. (A-T, C-G) .
This separation forms a Y shape called replication fork and create semiconservative replication. The two separated
strands then will act as templates to create new strands.
One of the strands is known as the leading strands while the other one known as lagging strand.
- Leading strand is oriented 5' to 3' direction toward the replication fork.
- Lagging strand is oriented 5' to 3' direction away from the replication fork.
Leading Strand
- A short pieces of RNA called primer produced by ezyme primase bind to the end of the leading strand. The primer acts as the starting point for DNA synthesis.
- DNA polymerase binds to the leading strand, adding new complementary nucleotide bases. (A,C,G,T) to the strand of DNA of the 5' 3' direction. This replication is called continuous.
Lagging Strand
- Numerous RNA primers bind at various point of along the strands.
- Chunks of DNA, called Okazaki fragments, are then added to the lagging strand also in 5' to 3' direction.
- This sort of replication is called discontinuous.
Then, DNA polymerase synthesizes the new strands by adding nucleotides that complement each strand. DNA replication occurs during the S-stage of interphase.
There are about 5 types of DNA polymerase involved in DNA replication:
- DNA-Pol I : repair and patching of DNA.
- DNA-Pol III : responsible for the polymerization of the newly formed DNA strand.
- DNA-Pol II, IV and V : proofreading and repair enzymes.
PRIMASE
When the strands have proven that there are no mistakes in the new DNA sequences, finally, an enzyme called DNA ligase seals up the sequence of DNA into two continuous double strands. DNA replication produced two DNA molecules consisting of one new and one old chain of nucleotides (semi-conservative). Lastly, the new DNA will automatically winds up into a double helix.
- catalyzes the copying of a short stretch of DNA template strand to produce RNA primer sequence.
When the strands have proven that there are no mistakes in the new DNA sequences, finally, an enzyme called DNA ligase seals up the sequence of DNA into two continuous double strands. DNA replication produced two DNA molecules consisting of one new and one old chain of nucleotides (semi-conservative). Lastly, the new DNA will automatically winds up into a double helix.
Here is the video of how DNA replication occurs :

















