DNA TRANSLATION


Translation is the process in which ribosomes in a cell's
cytoplasm create proteins, following transcription of DNA to RNA in the cell's
nucleus. The entire process is a part of gene expression.
THE GENETIC CODE
THIS
PROCESS INVOLVES SEVERAL KEY MOLECULES:
- mRNA Codon
- Ribosome (rRNA)
- tRNA anticodon
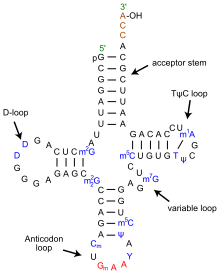
- The release factor
Translation proceeds in four phases:
- Amino acid activation:the amino acids (aa) are attached to their corresponding tRNA. The coupling reactions are catalysed by a group of enzymes called aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases (named after the reaction product aminoacyl-tRNA or aa-tRNA).


- Initiation: The ribosome assembles around the target mrna.
The first trna is attached at the start codon.


- Elongation: The trna transfers an amino acid to the trna corresponding
to the next codon. The ribosome then moves (translocates) to the next mrna codon
to continue the process, creating an amino acid chain.

- Termination: When a stop codon is reached, the ribosome
releases the polypeptide.

OVERVIEW OF DNA TRANSLATION



No comments:
Post a Comment